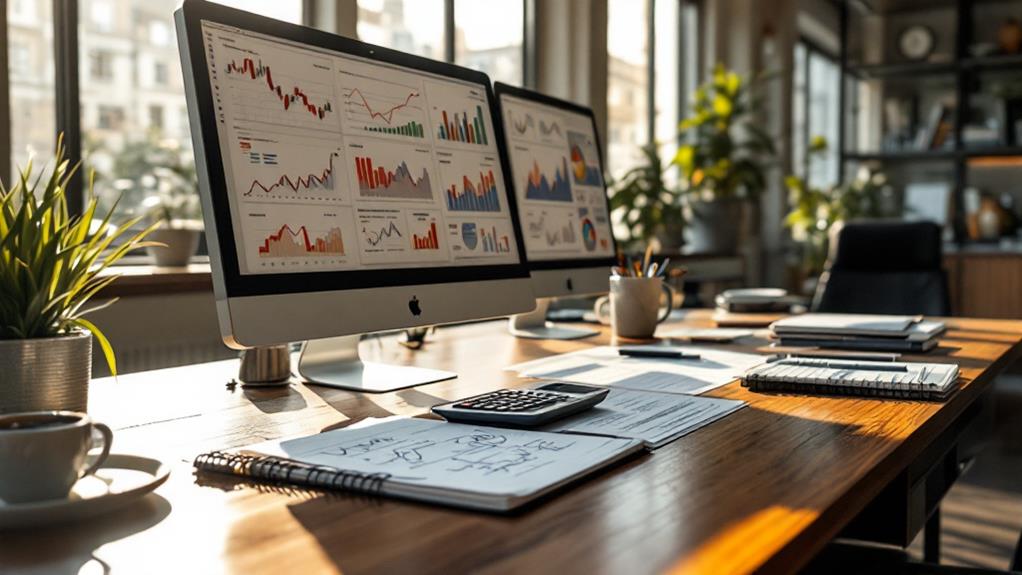
Revenue margins are a critical metric for evaluating your business's profitability after covering all expenses. By examining various types of margins, you can gain insights into different aspects of financial health. The gross profit margin looks at revenue after accounting for the cost of goods sold, offering a view of production efficiency. The operating profit margin, meanwhile, includes operating expenses, providing a broader perspective. The net profit margin, however, considers all expenses, painting a detailed picture of profitability. Analyzing these margins using tools like accounting software or spreadsheet applications reveals trends and guides strategic decisions, revealing deeper insights.
Understanding Revenue Margins
Understanding revenue margins is essential for any business looking to maximize profitability. Revenue margins, often referred to as profit margins, measure how much of every dollar of revenue is retained as profit after accounting for expenses. This metric provides insights into a company's financial health and efficiency.
By analyzing revenue margins, you can identify cost-saving opportunities, optimize pricing strategies, and enhance overall profitability.
To calculate revenue margins, you'll need to understand the difference between gross, operating, and net profit margins. The gross profit margin focuses on revenue remaining after deducting the cost of goods sold (COGS). It highlights production efficiency and indicates whether your pricing strategy covers direct costs.
Operating profit margin, on the other hand, takes into account operating expenses like wages and rent, offering a broader view of operational efficiency. Finally, the net profit margin considers all expenses, including taxes and interest, reflecting the overall profitability of the business.
Monitoring these metrics regularly allows you to make informed decisions. If your margins are shrinking, it's a signal to review cost structures or pricing. Conversely, healthy margins might indicate room for investment or expansion.
Understanding these metrics guarantees you maintain a competitive edge.
Basics of Drop Shipping
Drop shipping is a retail fulfillment method where a store doesn't keep the products it sells in stock. Instead, when you sell a product, you purchase the item from a third party and have it shipped directly to the customer.
This model can be quite appealing due to its low startup costs and minimal risk. Without the need to handle physical inventory, you can focus more on marketing and customer service. Some bulk purchasing discounts are available when buying from selected suppliers, which can help boost your revenue margins.
Here are some key aspects to take into account when starting a drop shipping business:
- Supplier Selection: Choose reliable suppliers that offer quality products and timely shipping. Your supplier's performance directly impacts your brand's reputation.
- Profit Margins: Since drop shipping involves purchasing from a third party, your profit margins might be lower compared to traditional retail. It's vital to price your products strategically to cover costs and generate profit.
- Inventory Management: Although you don't hold inventory, managing virtual stock levels with suppliers is essential to avoid selling out-of-stock items.
- Customer Experience: Guarantee seamless communication and transparency with customers regarding shipping times and product availability. Customer satisfaction is key to sustaining your business.
Furniture Reselling Models
How do furniture reselling models differ from traditional retail methods? In traditional retail, you purchase inventory upfront, store it, and sell it at a markup. This can tie up capital and require significant storage space. Furniture reselling models, however, often leverage digital platforms and on-demand inventory systems, reducing overhead. You might operate through consignment, where you sell furniture on behalf of owners and earn a commission, or through online marketplaces.
These models offer flexibility and can adapt to market trends more quickly. Here's a comparison of key attributes between traditional retail and furniture reselling models:
| Attribute | Traditional Retail | Furniture Reselling Models |
|---|---|---|
| Inventory Management | High upfront cost | Low to no upfront cost |
| Storage Requirements | Significant | Minimal |
| Revenue Model | Direct sales profit | Commission or fees |
| Market Adaptability | Slower | Faster |
In furniture reselling, you can utilize platforms like eBay or specialized sites to reach broader audiences without the need for physical storefronts. This model can boost your revenue margins by minimizing costs associated with storage and inventory. By understanding these differences, you can make informed decisions on which model aligns best with your business goals and resources.
Cost Components in Drop Shipping
When exploring the cost components in drop shipping, it's vital to recognize that this model greatly reduces the traditional costs associated with inventory management.
You don't need to maintain a warehouse or handle product storage, which greatly cuts down overhead. However, understanding all cost factors is important for effective financial planning.
1. Product Costs: Since you purchase products directly from suppliers, the cost per item can be higher than wholesale prices. This affects your profit margins but eliminates the upfront cost of bulk buying.
2. Shipping Fees: Although suppliers handle shipping logistics, you're often responsible for these costs, which can vary based on product size, weight, and destination.
These fees need careful consideration to avoid eroding profits.
3. Platform Fees: If you sell through online marketplaces like Amazon or eBay, you're subject to listing and transaction fees.
These can accumulate quickly, so factor them into your pricing model.
4. Payment Processing Fees: Platforms like PayPal or Stripe charge fees for processing payments.
These are generally a small percentage of each transaction but add up over time, impacting your revenue.
Pricing Strategies for Profit
Understanding the cost components in drop shipping lays the groundwork for effective pricing strategies that can maximize profits. By knowing your costs, you can set prices that cover expenses and generate a healthy margin.
Start by identifying your total cost, including product, shipping, and transaction fees. Then, consider your target profit margin, which is the difference between the selling price and total costs.
One approach is cost-plus pricing, where you add a markup to your total cost. This straightforward method guarantees costs are covered, but you must also consider market trends and competitor prices.
Dynamic pricing, which adjusts prices based on demand, competition, and other factors, might also be effective. This approach requires constant market monitoring but can optimize revenue by reacting to market conditions in real-time.
Penetration pricing, setting lower prices initially to attract more customers, can increase market share quickly. However, make sure you have a plan to gradually increase prices without losing customers.
Avoid underpricing, as it could devalue your products and harm profitability. Always keep an eye on the balance between staying competitive and maintaining a sustainable profit margin to guarantee long-term success.
Supplier Negotiation Tactics
Building strong supplier relationships is vital for maximizing your profit margins in drop shipping. Negotiating effectively with suppliers can greatly impact your bottom line. Here are some supplier negotiation tactics you can use to guarantee favorable terms:
- Research and Compare: Before entering negotiations, gather data on multiple suppliers. Compare prices, minimum order quantities, and shipping times. This information gives you leverage to negotiate better terms.
- Communicate Clearly: Be transparent about your business needs and goals. Explain your order volume and long-term potential to persuade suppliers to offer you better rates or terms.
- Build Rapport: Establish a relationship based on trust and mutual benefit. Regular communication and showing appreciation for the supplier's role in your success can foster goodwill, making them more amenable to negotiations.
- Negotiate Payment Terms: Cash flow is essential in drop shipping. Try negotiating for extended payment terms, such as net 30 or net 60, to improve your cash flow management.
Marketing to Maximize Revenue
Consistently refining your marketing strategies is vital if you want to maximize revenue in your drop shipping business. One effective approach is leveraging digital advertising platforms, like Google Ads and Facebook Ads, which allow you to target specific demographics, interests, and behaviors.
This precision guarantees that your products reach potential customers who are most likely to convert, thereby increasing your return on investment (ROI).
Email marketing is another powerful tool. By segmenting your email list, you can tailor messages to different customer groups, enhancing engagement and boosting sales.
Personalization, such as using recipients' names and recommending products based on past purchases, can greatly improve open and click-through rates.
Additionally, social media marketing plays an important role in revenue maximization. Platforms like Instagram and TikTok enable you to visually showcase products and engage with a larger audience.
Influencer partnerships can also amplify your reach, introducing your brand to new segments of the market.
Analyzing Market Trends
Keeping an eye on market trends is essential for staying ahead in the drop shipping industry. You need to understand what's driving consumer behavior and how to adapt your strategies accordingly. By analyzing market trends, you can identify new opportunities, anticipate shifts in demand, and make informed decisions that boost your revenue margins.
Here are four key steps to guide your analysis:
- Monitor Consumer Preferences: Track changes in consumer tastes and preferences. Use tools like Google Trends to see what's gaining popularity and adjust your product offerings to meet these demands.
- Evaluate Competitor Strategies: Analyze what your competitors are doing. Look at their pricing, marketing tactics, and product selections. This helps you identify gaps in the market that you can exploit.
- Analyze Economic Indicators: Stay informed about economic factors such as inflation rates, employment data, and consumer confidence indices. These indicators can impact purchasing power and influence demand.
- Leverage Social Media Insights: Social media platforms are a goldmine for trend analysis. Use them to gather insights on emerging trends, customer feedback, and influencer marketing strategies.
Reducing Operational Costs
When it comes to maximizing profitability in the drop shipping industry, reducing operational costs is essential. You need to assess several areas, from supplier negotiations to shipping efficiencies, to shave off unnecessary expenses. Begin by analyzing your current suppliers. Are you getting the best rates possible? Contemplate bulk ordering or establishing long-term contracts that could lead to discounts. Shipping is another critical area where costs can spiral. Partner with reliable carriers, and leverage technology to track shipments and optimize routes.
Additionally, evaluate your technology stack. Are you paying for software tools that overlap in functionality? Streamlining your tech can lead to significant savings. Also, look into automating repetitive tasks, freeing up time and reducing errors.
Below is a sample table highlighting areas to contemplate for cost reduction:
| Area | Action | Potential Savings |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Negotiations | Bulk ordering | 5-10% |
| Shipping Efficiencies | Route optimization | 3-7% |
| Technology Stack | Streamline tools | 10-15% |
| Task Automation | Automate repetitive tasks | Time and labor |
| Inventory Management | Just-in-time inventory | Reduced holding costs |
Tools for Margin Analysis
Understanding your revenue margins is essential, and employing the right tools for margin analysis can make this task straightforward. You need to assess your costs and revenues accurately, and using specific tools can simplify this complex process. Margin analysis tools help identify where your business is profitable and where improvements are needed.
- Spreadsheet Software: Excel or Google Sheets allow you to input data and use formulas to calculate margins quickly. These tools are flexible and can be customized to fit your specific needs.
- Accounting Software: Programs like QuickBooks or Xero provide built-in features for margin analysis. They automate data collection from your sales and expenses, offering detailed reports on your financial performance.
- Business Intelligence Tools: Platforms like Tableau or Power BI deliver advanced analytics capabilities. They help visualize data trends over time, making it easier to spot changes in your revenue margins.
- Cost Accounting Systems: These systems focus on detailed cost tracking. They provide insights into specific cost drivers, enabling you to identify areas where you can reduce expenses to improve margins.
Each tool has its strengths, so choose one that aligns with your business needs, ensuring a thorough analysis of your revenue margins.